- +86 15383000851
- +86 15303238802
- admin@hebeianda.cn
Your Location:Home >Products >API >55981-09-4
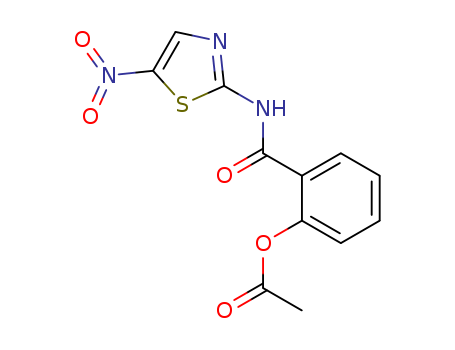

pd_meltingpoint:202 °C
Appearance:Crystalline Solid
Purity:99%
|
Description |
Nitazoxanide (NTZ), a thiazolide compound is a antiparasitic drug with structure similar to niclosamide, has been approved as an orphan drug for the treatment of diarrhea in children (age, 1–11 years) and is associated with giardiasis, but it also is approved for diarrhea caused by crytosporidiosis in patients with AIDS. Crytosporidiosis is a protozoal infection caused by Cryptosporidi um parvum. The condition is uncommon in healthy individuals but can be life-threatening in immunosuppressed patients and those with HIV infections. |
|
Chemical Properties |
Crystalline Solid |
|
Originator |
Alinia,Romark Laboratories, L.C. |
|
Uses |
A synthetic broad-spectrum antiparasitic nitroheterocycle (2-acetyloxy- N-(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl) benzamide), formulated for oral use. Nitazoxanide has been used: to test its anti-viral activity against chikungunya virusas an antiprotozoal agent to test its effect on cell viability in various cancer cell linesto test its effect on human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infected human fibroblast HFF cells. It is indicated for the treatment of diarrhea caused by G. lamblia or C. parvum. |
|
Manufacturing Process |
To a solution containing one mole p-metoxy-benzoyl chloride and one mole of carefully purified 2-amino-5-nitro-triazole in 200 ml of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran, one mole of triethylamine has been slowly added (about 10 minutes) while stirring. The reaction mixture, which became slightly warm, was stirred during 45 minutes and then poured under agitation, into 2 liters of distilled water. The stirring was continued until the precipitation of salicylamide, N-(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)-, acetate (ester) was complete. The obtained precipitate was dried, washed with water, dried again and recrystallized from methanol. The yield about 60%; melting point 202°C. |
|
Brand name |
Alinia (Romark). |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Anthelmintic |
|
Antimicrobial activity |
In vitro Cryptosporidium parvum sporocytes and oocysts are inhibited by <33 μm, and Giardia lamblia (intestinalis) trophozoites by <10 μm. The metabolite tizoxanide is more active than the parent compound against some isolates. E. histolytica is inhibited by 6–23 μm (parent compound) and 5.6– 28 μm (metabolite), and T. vaginalis by 0.5–15.5 μm (parent compound) and 0.3–12.2 μm (metabolite). Activity against other micro- organisms, including some helminths, bacteria (Clostridium difficile) and viruses (hepatitis C) has also been demonstrated. |
|
Acquired resistance |
Resistance caused by altered expression of genes involved in stress response has been demonstrated in experimental studies with G. lamblia. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Nitazoxanide is an inhibitor of pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR); Antimicrobial recently found to kill both non-replicating and replicating mycobacteria. FDA approved anti-parasitic drug (2002). Recent work (C & EN Sept. 14, 2009, p. 28) highlights that NTZ kills non-replicating and replicating TB bacteria and no apparent resistance is detected. |
|
Mechanism of action |
Nitazoxanide is a pro-drug that is metabolically converted into the deactylated drug tizoxanide (TIZ). The TIZ then undergoes a four-electron reduction of the 5-nitro group giving various short-lived intermediates, which may include the hydroxylamine derivative. It is these reduced products that represent the active form of NTZ. Whereas these intermediates would suggest that NTZ has the same mechanism of action as metronidazole, this does not appear to be the case. Nitazoxanide is thought to inhibit the enzyme pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase in Trichomonas vaginali s, Entamoeba histolytica, and Cl ostridium perfingens. The results of this inhibition is disruption of the bioenergetics of these organisms. Unlike metronidazole and tinidazole, which fragment DNA and are suspected mutagenic agents, NTZ and TIZ do not cause DNA fragmentation and are not considered to be mutagenic. This might be associated with the higher redox potential found for NTZ, a nitrothiazole, in comparison with very low redox potential found for the nitroimidazoles, such as metronidazole and tinidazole. Additional metabolites of TIZ also includes the glucuronide, which shows some biological activity, and small amounts of an aromatic hydroxylation product. |
|
Pharmacokinetics |
After oral administration the major circulating metabolites are tizoxanide (desacetyl nitazoxanide) and its glucuronide. Minor metabolites include salicyluric acid and tizoxanide sulfate. Maximum concentrations of the active metabolites tizoxanide and tizoxanide glucuronide are observed within 1–4 h. Following a single oral dose of 500 mg given with food, the Cmax of both metabolites was around 10 mg/L. Tizoxanide has a halflife of around 1–2 h and is >99.9% bound to plasma proteins. |
|
Side effects |
Nitazoxanide appears well tolerated. Side effects may include abdominal pain diarrhea, headache and nausea. |
|
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments |
Nitazoxanide oral paste is indicated for the treatment of horses with equine protozoal myeloencephalitis (EPM) caused by Sarcocystis neurona. In humans, nitazoxanide is approved (in the USA) for use in treating diarrhea caused by Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia lamblia in pediatric patients from ages 1 to 11 years old. Because of the drug’s spectrum of activity and apparent safety, there is considerable interest in using it in a variety of companion animal species, but data is lacking for specific indications and dosages. |
|
Metabolism |
Nitazoxanide is available as powder that is reconstituted and dispensed as an oral suspension. The drug is well absorbed from the GI tract and rapidly metabolized, with elimination products appearing in the urine and feces. The only identified products in the plasma are TIZ and its glucuronide. The product can be taken with food. |
InChI:InChI=1/C12H9N3O5S/c1-7(16)20-9-5-3-2-4-8(9)11(17)14-12-13-6-10(21-12)15(18)19/h2-6H,1H3,(H,13,14,17)
During the last years, the progression t...
The invention relates to thiazole compou...
A novel and efficient method for the reg...
-
C13H10N2O5S

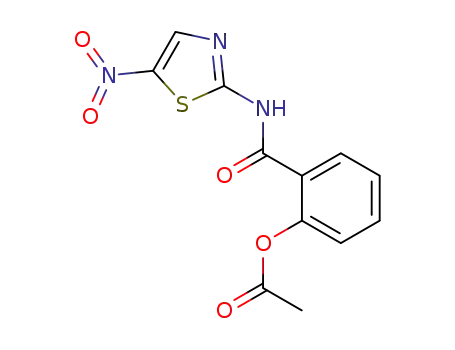
nitazoxanide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With nitronium tetrafluoborate; silver carbonate; In N,N-dimethyl acetamide; at 90 ℃; for 12h; regioselective reaction; Inert atmosphere; Schlenk technique;
|
71% |
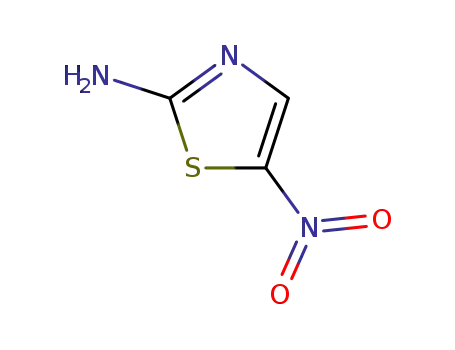
2-amino-5-nitro-1,3-thiazole
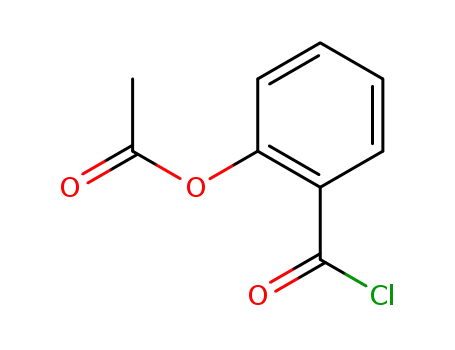
O-acetylsalicyloyl chloride


nitazoxanide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|

2-amino-5-nitro-1,3-thiazole

O-acetylsalicyloyl chloride
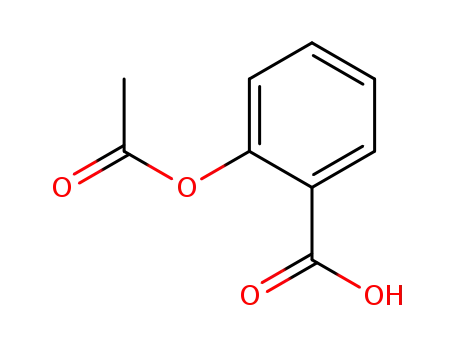
aspirin
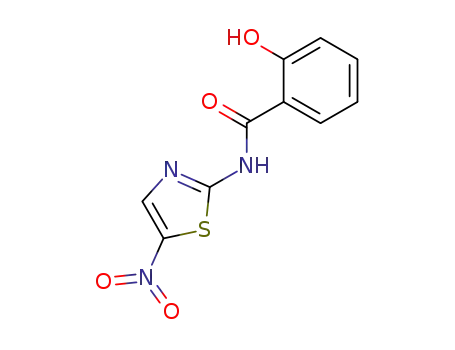
tizoxanide
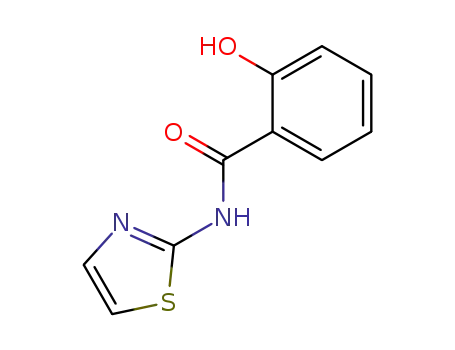
RM4857
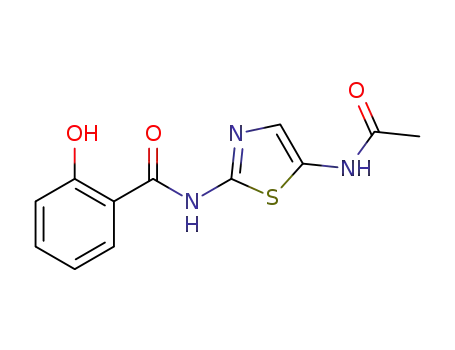
(2-hydroxybenzoyl)-N-(5-acetamidothiazol-2-yl)amine
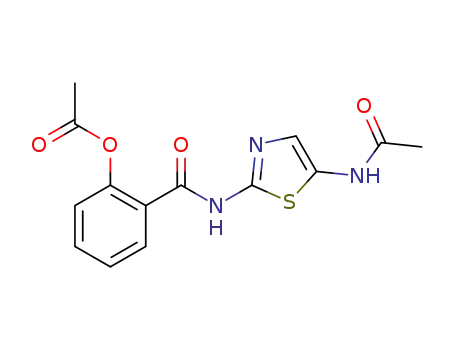
C14H13N3O4S
CAS:868844-74-0
CAS:52-90-4
CAS:118-42-3
CAS:13488-22-7