- +86 15383000851
- +86 15303238802
- admin@hebeianda.cn
Your Location:Home >Products >API >11113-50-1

pd_meltingpoint:170.9oC
Appearance:White powder
Purity:99%
|
Chemical Properties |
Boric acid is a weak acid (pKa = 9.15), existing in aqueous solutions at or below pH 7 as undissociated boric acid. In the solid there is considerable hydrogen bonding between H3BO3 molecules resulting in a layer structure, which accounts for the easy cleavage of the crystals. H3BO3 molecules also exist in dilute solutions but in more concentrated solutions polymeric acids and ions are formed (e.g. H4B2O7; pyroboric acid or tetrahydroxomonoxodiboric(III) acid). The compound is a very weak acid but also acts as a Lewis acid in accepting hydroxide ions: B(OH)3 + H2O→B(OH)4 - + H+If solid boric acid is heated it loses water and transforms to another acid at 300℃. This is given the formula HBO2 but is in fact a polymer (HBO2)n. It is called metaboric acid or, technically, polydioxoboric(III) acid. |
|
Physical properties |
Boric acid exists in the form of colorless crystals or as a white powder and is soluble in water. It occurs naturally in the condensate from volcanic steam vents (suffioni). Commercially, it is made by treating borate minerals (e.g. kernite, Na2B4O7.4H2O) with sulphuric acid followed by recrystallization. |
|
Uses |
Boric acid is used in the manufacture of glass (borosilicate glass), glazes and enamels, leather, paper, adhesives, and explosives. It is widely used (particularly in the USA) in detergents, and because of the ability of fused boric acid to dissolve other metal oxides it is used as a flux in brazing and welding. Because of its mild antiseptic properties it is used in the pharmaceutical industry and as a food preservative.boric acid is an effective preservative against yeast. It is used in concentrations of 0.01 to 1.0 percent and has fair to good antiseptic properties. It may also be used as a buffer and denaturant. Boric acid is prepared from sulfuric acid and natural borax. It can cause skin rashes and irritation if used in high concentrations. The use of boric acid in cosmetic preparations is no longer very popular. The primary industrial use of boric acid is in the manufacture of monofilament fiberglass usually referred to as “textile fiberglass”. Textile fiberglass is used to reinforce plastics in applications that range from boats, to industrial piping to computer circuit boards. Boric acid is used in nuclear power plants to slowdown the rate at which fission is occurring. Fission chain reactions are generally driven by the amount of neutrons present (as products from previous fissions). Boric acid is used in producing the glass faceplates of LCD flat panel displays. In electroplating, boric acid is used as part of some proprietary formulas. It is also used in the manufacturing of “remming mass”, a fine silica-containing powder used for producing induction furnace linings. Borates including boric acid have been used since the time of the Greeks for cleaning, preserving food, and other activities. It is used in pyrotechnics to prevent the amide-forming reaction between aluminum and nitrates. A small amount of boric acid is added to the composition to neutralize alkaline amides that can react with the aluminum. Boric acid dissolved in methane is popularly used among fire jugglers and fire spinners to create a deep green flame. Boric acid is added to salt in the curing of cattle hides, calfskins and sheepskins. Used in that way it helps to control bacteria development and also aids in the control of insects. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: Boric acid is a member of boric acids. It has a role as an astringent. It is a conjugate acid of a dihydrogenborate. |
|
Indications |
Boric Acid is a weakly acidic hydrate of boric oxide with mild antiseptic, antifungal, and antiviral properties. The exact mechanism of action of boric acid is unknown; generally cytotoxic to all cells. It is used in the treatment of yeast infections and cold sores.Boric acid, 600 mg in a gelatin capsule, used intravaginally daily for 14 days, has been reported effective even in resistant Candida infections. |
|
Preparation |
Boric acid is prepared by treating borax with nitric acid and nitric acid is chosen over hydrochloric acid because sodium nitrate is more readily soluble than sodium chloride, and sulphuric acid is hard to wash out so not employed.In laboratory boric acid is prepared from sodium borate.Na2B4O7 + H2SO4 + 5H2O→ Na2SO4 + 4H3BO3 |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
Boric acid is a long-standing traditional remedy with mainly antifungal and antimicrobial effects. For medicinal uses, it has become known as sal sedativum, which was discovered by Homberg, the Dutch natural philosopher, in 1702. Diluted solutions were and sometimes still are used as antiseptics for the treatment of athletes’ foot and bacterial thrush, and in much diluted solutions as eyewash. |
|
Agricultural Uses |
Boric acid is used as an insecticide for controlling house holding pests like termites, ants, and small insects. Boric acid (H3BO3) is one of the boron-containing nutrients added to fertilizers. It contains around 17% boron. A solution of boric acid and water is used as a foliar spray to overcome boron deficiency. |
|
Potential Exposure |
Boric acid is a fireproofing agent for wood; a preservative, and an antiseptic. It is used in the manufacture of glass, pottery, enamels, glazes, cosmetics, cements, porcelain, borates, leather, carpets, hats, soaps; artificial gems; in tanning leather; printing, dyeing, painting, and photography. |
|
Shipping |
UN 3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9—Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Boric acid decomposes in heat above 100 C, forming boric anhydride and water. Boric acid is hygroscopic; it will absorb moisture from the air. Boric acid aqueous solution is a weak acid; incompatible with strong reducing agents including alkali metals and metal hydrides (may generate explosive hydrogen gas); acetic anhydride, alkali carbonates, and hydroxides. Violent reaction with powdered potassium metal, especially if impacted. Attacks iron in the presence of moisture. |
|
Waste Disposal |
Boric acids may be recovered from organic process wastes as an alternative to disposal. |
|
Who Evaluation |
Evaluation year: 1961 |
InChI:InChI=1/BH3O3/c2-1(3)4/h2-4H
Tetraborane-8 carbonyl (B4H8CO) is made ...
Lead oxide is an important glass modifie...
Heating of the recently described compou...
Trimetallic NiFePd nanoparticles (NPs) a...
In acid media (+> = 0.02-0.2 mol dm-3), ...
The electrical and magnetic properties o...
Single crystals of pure aluminoborate PK...
The preparation of solid H2B2S5 and its ...
-
Octachlorononaborane-9, B9Cl8H, is a vol...
B4 C submicron particles were obtained b...
-
To gain insight on the mechanistic aspec...
A BH3-containing species, which is a rel...
The development of noninvasive methodolo...
Since moisture may frequently be present...
The dihydrate and diethanolate of dibora...
Water, methanol and isopropylamine react...
The kinetics of reduction of silver(II) ...
A profluorescent probe that has no fluor...
Hydrazine borane (N2H4BH3, 15.4 wt% H) h...
Reactions of decaborane with various ald...
The new boron hydride anions 10-R-B19H19...
The efficient production of H2 from hydr...
Designing highly efficient catalysts for...
phosphorus(V) chloride * 2 BBr3

hydrogenchloride
phosphoric acid

hydrogen bromide

boric acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With moist air; In neat (no solvent); hydrolysis with moist air under formation of H3PO4, H3BO3 and evolution of HCl and HBr;;
|
boron trioxide


boric acid

metaboric acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With nitric acid; HNO3 conc. between 60-94%;
|
|
|
With HNO3; HNO3 conc. between 60-94%;
|
|
|
With H2O; heating in vap. H2O;
|
5-bromo-2-chloropyridine
pyrographite
triacetoxyborane
dihydrogen peroxide
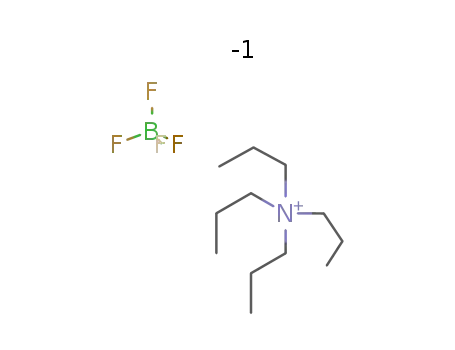
Tetrapropylammonium tetrafluoroborate
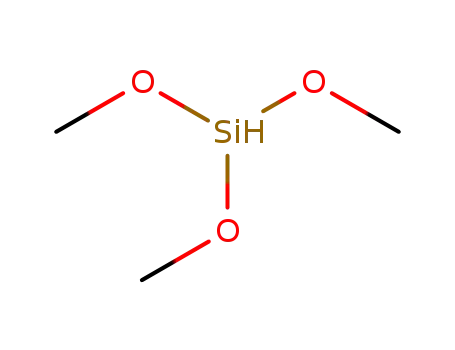
trimethoxysilane
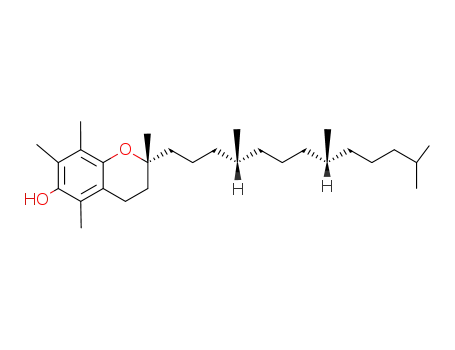
Tocopherol
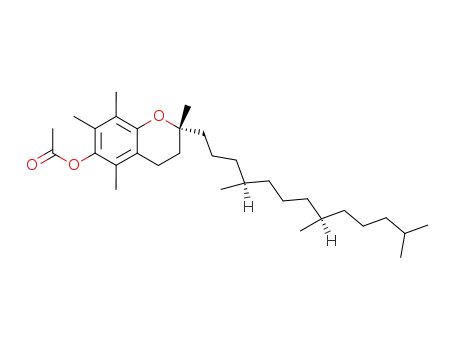
RRR-α-tocopheryl acetate
CAS:69430-36-0
CAS:1451-83-8
CAS:7681-11-0
CAS:77614-16-5