- +86 15383000851
- +86 15303238802
- admin@hebeianda.cn
Your Location:Home >Products >Chemical Reagents >1120-71-4
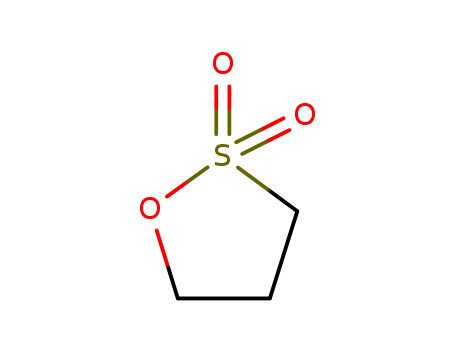

pd_meltingpoint:30-33 °C(lit.)
Appearance:Clear crystals
Purity:99%
|
Description |
Propane sultone also known as 1,3-propane sultone was first produced in the United States in 1963. Propane sultone exists at room temperature as a colorless liquid with a foul odor or as a white crystalline solid. |
|
Chemical Properties |
1,3-Propane sultone is a white crystalline solid or a colorless liquid above 30°C. It releases a foul odor as it melts. It is readily soluble in water and many organic solvents such as ketones, esters and aromatic hydrocarbons. |
|
Uses |
1,3-Propane sultone is used as a chemical intermediate to introduce the sulfopropyl group into molecules and to confer water solubility and an anionic character to the molecules. It is used as a chemical intermediate in the production of fungicides, insecticides, cation-exchange resins, dyes, vulcanization accelerators, detergents, lathering agents, bacteriostats, and a variety of other chemicals and as a corrosion inhibitor for mild (untempered) steel. |
|
Application |
1,3-Propanesultone is a cyclic sulfonic ester mainly used to introduce a propane sulfonic functionality into the organic structure. It has been used in preparation of poly[2-ethynyl-N-(propylsulfonate)pyridinium betaine],novel poly(4-vinylpyridine) supported acidic ionic liquid catalyst,novel poly(4-vinylpyridine) supported acidic ionic liquid catalyst.1,3-Propanesultone can be used to synthesize:A sulfonic acid functionalized acidic ionic liquid modified silica catalyst that can be used in hydrolysis of cellulose.Zwitterionic-type molten salts with unique ion conductive properties.Zwitterionic organofunctional silicones by the quaternization of organic amine functional silicones. |
|
Preparation |
1,3-propane sultone is produced commercially by dehydrating gamma-hydroxy-propanesulfonic acid, which is prepared from sodium hydroxypropanesulfonate. this sodium salt is prepared by addition of sodium bisulfite to allyl alcohol. |
|
Definition |
1,3-Propane sultone is a sultone. It is used as a chemical intermediate. When heated to decomposition, it emits toxic fumes of sulfur oxides. Humans are potentially exposed to residues of 1,3-propane sultone when using products manufactured from this compound. The primary routes of potential human exposure to 1,3-propane sultone are ingestion and inhalation. Contact with this chemical can cause mild irritation of the eyes and skin. It is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen. |
|
General Description |
Propanesultone is a synthetic, colorless liquid or white crystalline solid that is readily soluble in water and many organic solvents such as ketones, esters and aromatic hydrocarbons. Melting point 86°F. Releases a foul odor when melting. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Soluble in water [Hawley]. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
1,3-Propanesultone reacts slowly with water to give 3-hydroxopropanesulfonic acid. This reaction may be accelerated by acid. May react with strong reducing agents to give toxic and flammable hydrogen sulfide. |
|
Hazard |
Possible carcinogen. |
|
Health Hazard |
Propane sultone is a carcinogen in experimental animals and a suspected human carcinogen. No human data are available. It is a carcinogen in rats when given orally, intravenously, or by prenatal exposure and a local carcinogen in mice and rats when given subcutaneously. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Safety Profile |
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, tumorigenic, and teratogenic data. Poison by subcutaneous route. Moderately toxic by skin contact and intraperitoneal routes. Human mutation data reported. Implicated as a human brain carcinogen. A slun irritant. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx. |
|
Potential Exposure |
A potential danger to those involved in use of this chemical intermediate to introduce the sulfo- propyl group (-CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 SO 3-) into molecules of other products. |
|
Carcinogenicity |
1,3-Propane sultone is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals. |
|
Environmental Fate |
Routes and Pathways and Relevant Physicochemical Properties Appearance: white crystalline solid or colorless liquid. Solubilities: readily soluble in ketones, esters, and aromatic hydrocarbons; insoluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons; and soluble in water (100 g l-1). Partition Behavior in Water, Sediment, and Soil If 1,3-propane sultone is released to soil, it will be expected to rapidly hydrolyze if the soil is moist, based upon the rapid hydrolysis observed in aqueous solution. Since it rapidly hydrolyzes, adsorption to and volatilization from moist soil are not expected to be significant processes, although no data specifically regarding the fate of 1,3-propane sultone in soil were located. If released into water, it will be expected to rapidly hydrolyze. The produce of hydrolysis is 3-hydroxy- 1-propansulfonic acid. Since it rapidly hydrolyzes, bioconcentration, volatilization, and adsorption to sediment and suspended solids are not expected to be significant processes. If released to the atmosphere, it will be susceptible to photooxidation via vapor-phase reaction with photochemically produced hydroxyl radicals with a half-life of 8 days estimated for this process. |
|
Shipping |
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN2810 Toxic liquids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. |
|
Toxicity evaluation |
The reaction of propane sultone with guanosine and DNA at pH 6–7.5 gave an N7-alkylguanosine as the main product (>90%). Similar evidence suggested that two of the minor adducts were N1- and N6-alkyl derivatives, accounting for approximately 1.6 and 0.5% of the total adducts, respectively. N7- and N1-alkylguanine were also detected in the DNA reacted with propane sultone. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explo- sions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. |
|
EXPOSURE ROUTES |
inhalation, skin absorption, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact |
|
FIRST AID |
(See procedures) Eye:Irrigate immediately Skin:Water flush immediately Breathing:Respiratory support Swallow:Medical attention immediately |
InChI:InChI=1/C3H6O3S/c4-7(5)3-1-2-6-7/h1-3H2
The N-nitroso derivatives of propanesult...
Evidence is presented which indicates th...
The kinetics and mechanism of the oxidat...
The invention relates to a 1,3-propane s...
The invention discloses a solvent-free m...
The invention discloses a 1, 3 - propane...
The invention discloses a method for pre...
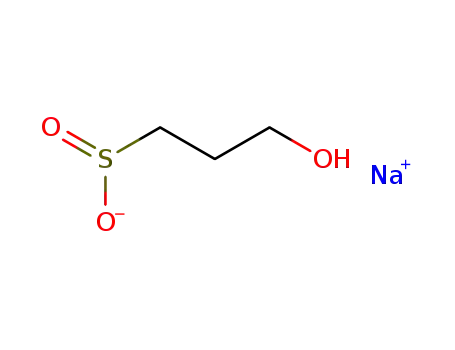
sodium 3-hydroxy-1-propanesulfinate

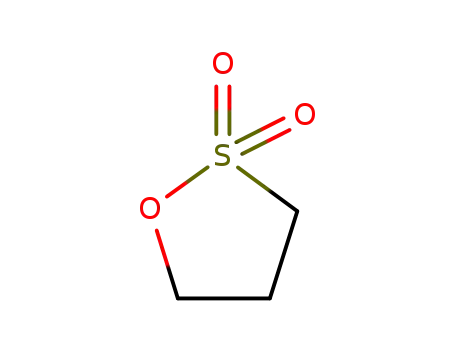
1,3-propanesultone
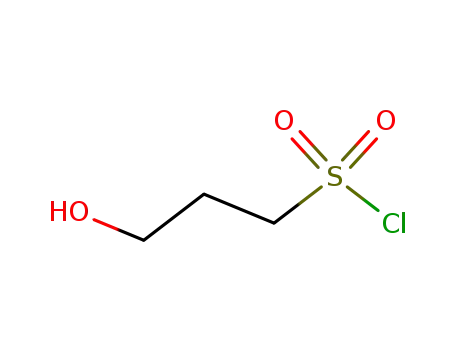
3-hydroxy-1-propanesulfonyl chloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
chlorine;
In
dichloromethane;
Yield given. Yields of byproduct given;
|
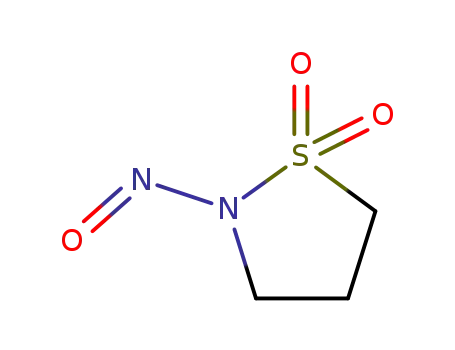
N-nitrosopropanesultam


1,3-propanesultone

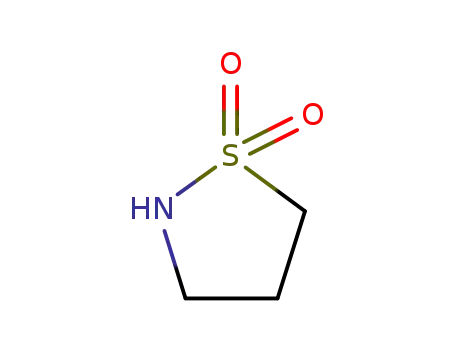
isothiazolidine 1,1-dioxide

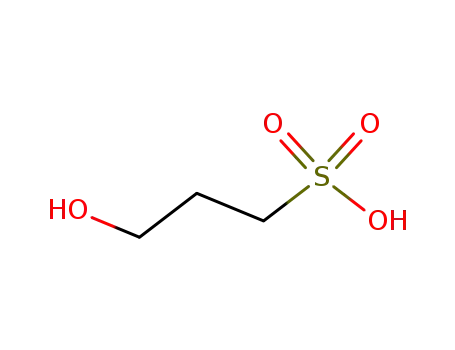
3-hydroxypropanesulfonic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
sodium carbonate;
In
chloroform;
Product distribution;
Heating;
other sultams, var. reagents;
|
18 % Spectr. 70 % Spectr. 5 % Spectr. |

3-hydroxypropanesulfonic acid
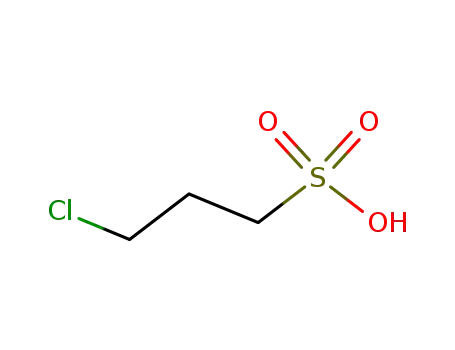
3-chloro-propane-1-sulfonic acid
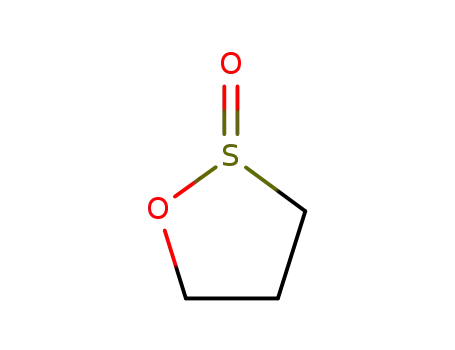
1,3-propanesultine
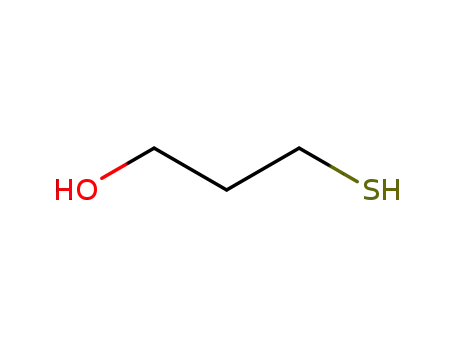
3-sulfanylpropanol
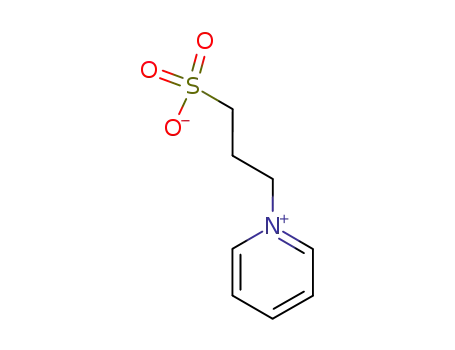
1-(3-sulfopropyl)pyridine
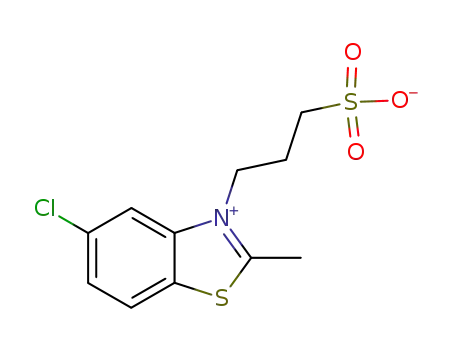
Anhydro-2-methyl-5-chlor-3<3'-sulfopropyl>-benzthiazoliumhydroxid
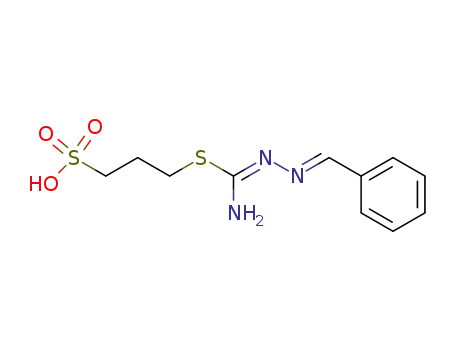
3-(amino-benzylidenehydrazono-methylsulfanyl)-propane-1-sulfonic acid
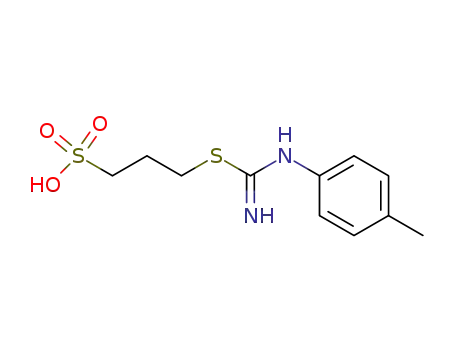
3-p-tolylcarbamimidoylmercapto-propane-1-sulfonic acid
CAS:868844-74-0
CAS:52-90-4
CAS:149635-73-4
CAS:221231-10-3