- +86 15383000851
- +86 15303238802
- admin@hebeianda.cn
Your Location:Home >Products >Chemical Reagents >120-61-6
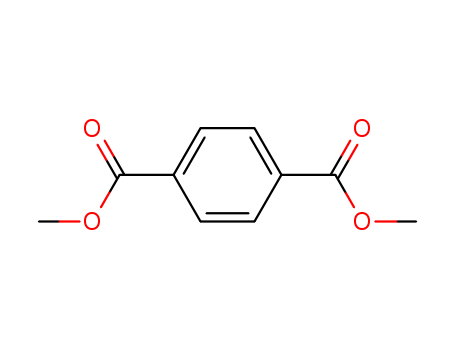

pd_meltingpoint:140 °C
Appearance:White needle crystal
Purity:99%
|
Description |
Dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO2CH3)2. It is the diester formed from terephthalic acid and methanol. It is a white solid that melts to give a distillable colourless liquid. |
|
Chemical Properties |
The empirical formula of dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) is C10H10O4. Its structural formula is 1,4-(COOCH3)2C6H4. At room temperature, exists as colorless crystals. DMT is soluble in ether and chloroform, slightly soluble in ethanol, and fairly insoluble in water (<1 g/L at 13℃). |
|
Uses |
Dimethyl terephthalate is used widely as an industrial intermediate to manufacture polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and dioctyl terephthalate (OECD, 2001).It is used in the Polyester Film (Audio/Video Tape,X-ray Film,Photo Film), Polyester Fiber, Pet Bottle, Polyester Adhesive, Engineering Plastics. DMT is volatile, it is an intermediate in some schemes for the recycling of PET. |
|
Production Methods |
Dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) has been produced in a number of ways. Conventionally and still of commercial value is the direct esterification of terephthalic acid. Alternatively, it can be prepared by alternating oxidation and methyl-esterification steps from p-xylene via methyl-p-toluate. |
|
Preparation |
Several processes have been developed for the preparation of dimethyl terephthalate from p-xylene, but the most important proceeds as follows: The oxidation steps are carried out in the liquid phase at about 170°C and 1.5 MPa (15 atmospheres) in the presence of a cobalt acetate or naphthenate catalyst whilst the esterifications are conducted at about 150°C. Dimethyl terephthalate may also be produced by esterification of terephthalic acid. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: Dimethyl terephthalate is a diester resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy groups of terephthalic acid with methanol. It is a primary ingredient widely used in the manufacture of polyesters and industrial plastics. It is a methyl ester, a diester and a phthalate ester. It derives from a terephthalic acid. |
|
Application |
Dimethyl terephthalate undergoes enzymatic polycondensation with 1,8-diaminooctane to yield oligo(octamethylene terephthalamide).Dimethyl terephthalate was used to synthesize silicone aromatic polyesters by the transesterification reaction with α,ω-bis(hydroxyalkyl)-terminated poly(dimethylsiloxane) in toluene. It was used in the synthesis of multiblock copolymers consisting of polyiso-butylene, dimethyl terephthalate and 1,4-butanediol. |
|
Synthesis Reference(s) |
Chemistry Letters, 15, p. 851, 1986Journal of the American Chemical Society, 111, p. 8742, 1989 DOI: 10.1021/ja00205a039Tetrahedron Letters, 17, p. 3299, 1976 |
|
General Description |
Dimethyl terephthalate appears as white solid or heated colorless liquid. Has no odor. Liquid solidifies in cool water. Solid and liquid sink in water. (USCG, 1999) |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
When mixed with air, the vapor or dust forms very hazardous and highly reactive mixtures. . Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
DIMETHYL TEREPHTHALATE is an ester. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. Can generate electrostatic charges. [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980. p. 250]. DIMETHYL TEREPHTHALATE is sensitive to heat. The molten material reacts with water due to the temperature. DIMETHYL TEREPHTHALATE is incompatible with strong oxidizers, strong acids and strong bases. |
|
Health Hazard |
Molten DMT will cause severe burns of skin on contact. |
|
Fire Hazard |
DIMETHYL TEREPHTHALATE is combustible. |
|
Safety Profile |
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Mdly toxic by ingestion. An eye irritant. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes |
|
Carcinogenicity |
In a study conducted by the NCI, DMT was not considered to be carcinogenic in rats or mice ingesting 2500 or 5000 ppm in the diet for 103 weeks. |
|
Purification Methods |
Purify it by recrystallisation from aqueous EtOH, MeOH or CCl4; or by zone melting. [Beilstein 6 H 843, 6 III 4250, 6 IV 3303.] . |
|
Consumer Uses |
ECHA has no public registered data indicating whether or in which chemical products the substance might be used. ECHA has no public registered data on the routes by which this substance is most likely to be released to the environment. |
InChI:InChI=1/C10H10O4/c1-13-9(11)7-5-3-4-6-8(7)10(12)14-2/h3-6H,1-2H3
Diverse functionalized aromatic compound...
A novel colorimetric chemosensor based o...
Polyethylene terephthalate that is 100 %...
Nitrosocarbonyl intermediates on solid p...
To date, Alzheimer's disease is the most...
Microporous and mesoporous zincosilicate...
Terephthalic acid can be readily convert...
New heteroaromatic benzene dicarboxamide...
-
A new protocol (Transfer Technology) is ...
-
When terephthalic acid, which had been c...
(Chemical Equation Presented) Whereas th...
Various aryl triflates derived from phen...
Oxidizing aromatics: We report an operat...
Palladium complexes immobilized onto gen...
A new protocol for the methoxycarbonylat...
Carboxyl methyltransferase (CMT) enzymes...
Homogeneous liquid-phase oxidation of a ...
The chlorination of aromatic carboxylic ...
The disclosure provides, inter alia, saf...
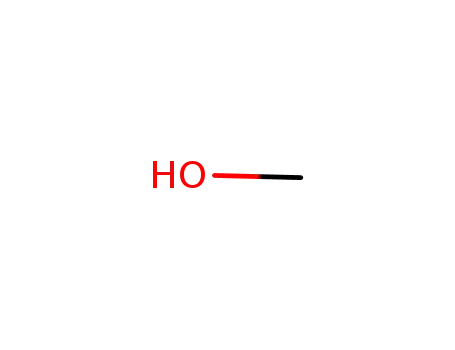
methanol
carbon monoxide

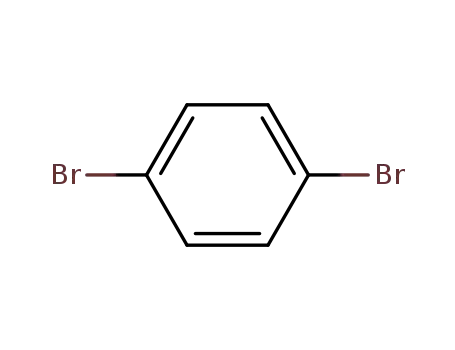
1.4-dibromobenzene

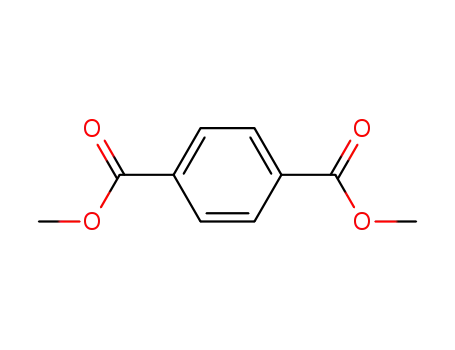
1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester

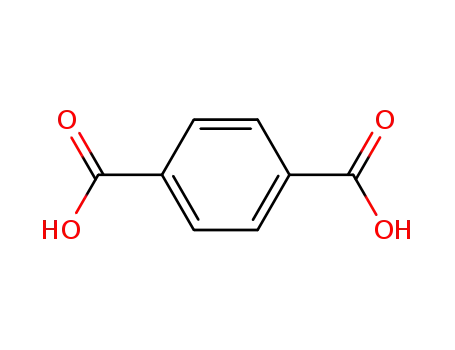
terephthalic acid

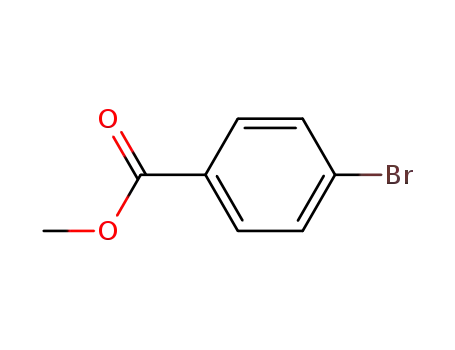
4-methoxycarbonylphenyl bromide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
tert-Amyl alcohol; sodium hydride;
cobalt(II) acetate;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 40 ℃;
for 14h;
under 760 Torr;
Irradiation;
|
6% 12% 80.5% |
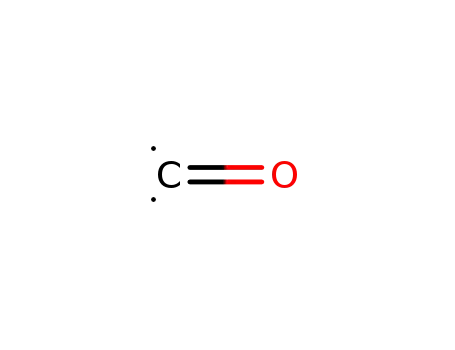
carbon monoxide

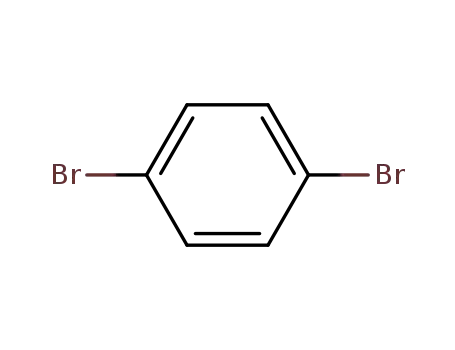
1.4-dibromobenzene


1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester


terephthalic acid


4-methoxycarbonylphenyl bromide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
methanol; tert-Amyl alcohol; sodium hydride;
cobalt(II) acetate;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 40 ℃;
for 14h;
under 760 Torr;
Irradiation;
|
80.5% 12% 6% |

diazomethane

terephthalic acid

methanol
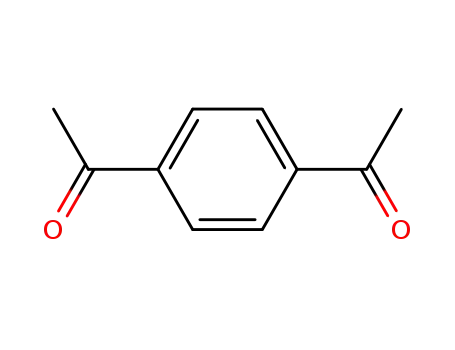
1,4-Diacetylbenzene
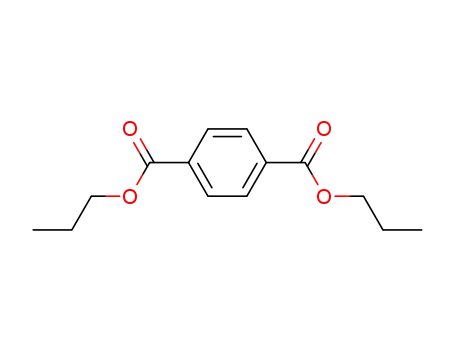
terephthalic acid dipropyl ester
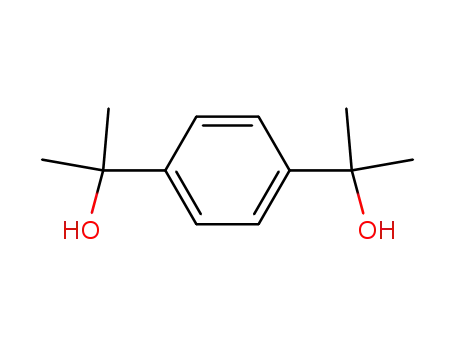
α,α,α',α'-tetramethyl-1,4-benzenedimethanol
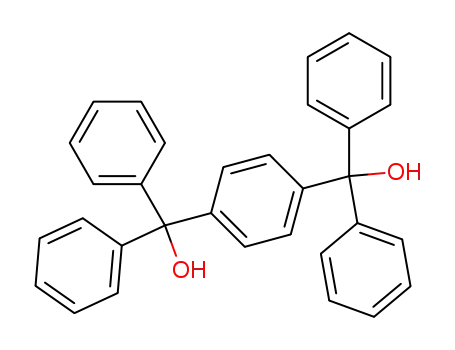
1,4-bis(diphenylhydroxymethyl)benzene
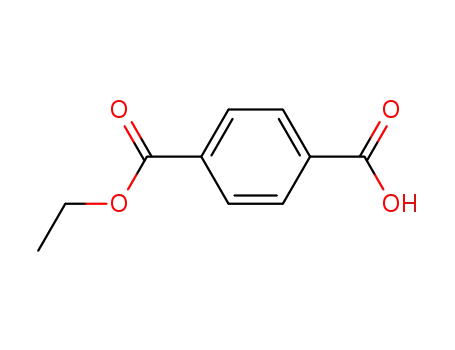
terephthalic acid monoethyl ester
CAS:119356-77-3
CAS:868844-74-0
CAS:67727-97-3
CAS:52-90-4