- +86 15383000851
- +86 15303238802
- admin@hebeianda.cn
Your Location:Home >Products >Biochemical Engineering >58-63-9
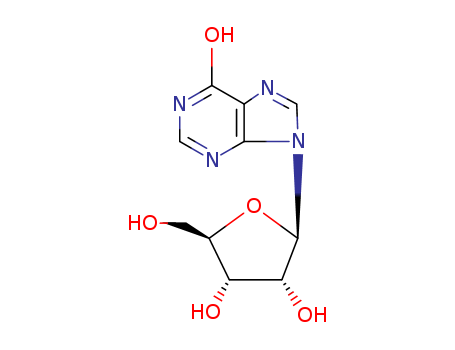

pd_meltingpoint:222-226 °C (dec.)(lit.)
Appearance:White crystalline powder
Purity:99%
|
Chemical Properties |
White crystalline powder |
|
Originator |
Foreart,Guarnieri,Italy,1970 |
|
Occurrence |
Inosine is a synthetic |
|
Uses |
Has neuroprotective properties improving axonal wiring. Has been used to treat stroke patients to restore neural function. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A purine nucleoside in which hypoxanthine is attached to ribofuranose via a beta-N9-glycosidic bond. |
|
Manufacturing Process |
As described in US Patent 3,049,536, inosine may be prepared starting with adenosine.The Deamination of Adenosine: 20 g of adenosine are dissolved in one liter of water by warming, and after cooling to room temperature 120 g of barium nitrite (monohydrate) are added to the solution. Under stirring there is added in time intervals of one hour 160 cc of 2 N sulfuric acid after each time interval. After the third addition, the reaction mass is allowed to stand for 3 hours at room temperature. The solution is then tested for barium, and if some barium is still present a slight excess of sulfuric acid is added. 300 cc of methanol is then added. In order to drive off the excess of nitrous acid, CO2 is conducted through the solution until the solution is free of nitrous acid as determined by testing with potassium iodide-starch paper. The precipitated barium sulfate is separated by centrifugation. The residue is washed one time with about 500 cc of water. The total volume of the centrifugate is about 2.3 liters.Isolation of Inosine by Ion Exchange Method: Half of the above clear centrifugate (1.15 liters) is treated with 250 cc of anion exchange (bicarbonate form) and stirred together therewith for 16 hours at room temperature. The pH value is increased thereby to about 4 to 5. The ion exchanger is filtered off under suction and washed 3 times, each time with 150 cc of water. The solution is brought to a pH value of 7 by means of normal sodium hydroxide (total volume of the solution about 1.55 liters), and concentrated to a volume of about 100 cc under vacuum.The inosine is crystallized overnight in an ice box and the inosine is then filtered off by suction, washed with a small amount of ice water and dried at a temperature of 105°C. A first fraction of crude inosine consisting of 5.4 g having a purity of 99% is obtained. Further fractions of crude inosine are obtained from the mother liquid by concentration, the total amount constituting 3.2 g having a purity of 96 to 98%. The yield of crude inosine is 8.6 g which is equal to 86%.Recrystallization of the Crude Inosine: 17.0 g of crude inosine are dissolved in 400 cc of 80% ethanol in a water bath, filtered while hot and brought to crystallization in an ice box. After standing overnight the crystalline material is filtered off under suction and washed with ice water. The pure inosine is dried in a drying chamber at a temperature of 105°C. The yield of pure inosine is 15.0 g which is equal to 75%. The yield can be further increased by workingup the mother liquor of the crystallization as set forth above.Alternatively, inosine may be made by fermentation as described in US Patent 3,111,459. 3 ml portions of a culture medium consisting of glucose (5 g/dl), ammonium chloride (0.4 g/dl), urea (0.4 g/dl), KH2PO4 (0.1 g/dl), MgSO4 · 7H2O (0.02 g/dl), Mn++ (2 ppm), Fe++ (2ppm), casein hydrolyzate (0.2 g/dl), yeast extract (0.2 g/dl), corn steep liquor (0.2 ml/dl), polypeptone (0.1 g/dl), meat extract (0.1 g/dl) and sodium ribonucleate (10 mg/dl) were poured into respective test tubes and each tube was sterilized at 115°C for 10 minutes. Thereafter separately sterilized calcium carbonate was added in the amount of 2 g/dl and then cells of Bacillus subtilis S26910 were inoculated into the above media and cultured with shaking at 30°C for 20 hours.The resulting culture liquids were utilized for seeding, 20 ml of the medium having the composition described above were poured into a 500 ml shaking flask and sterilized at 115°C for 10 minutes and five drops of the above seed were added, and then cultured with shaking at 30°C for 65 hours. Thereafter 0.15 g/dl of inosine were accumulated.The inosine-containing solution, which was obtained by separating the cells from the resulting fermentation liquid, was treated with both decolorizing resins and anion exchange resins by means of a conventional method and then acetone was added to crystallize the inosine. 1.47 g of the crude crystals of inosine were obtained from 3.5 liters of the culture liquid containing 1 g of inosine per liter. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Cardiotonic |
|
General Description |
Inosine is a non-canonical nucleotide majorly present as monophosphate. It has ability to base pair with deoxythymidine, deoxyadenosine and deoxyguanosine. Incorporation of inosine in place of guanine modulates translational events. Inosine has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective functionality. Inosine is prescribed as a therapeutic supplement for nerve injury, inflammation and oxidative stress. It modulates biological processes through adenosine receptors. Its enhances neurite outgrowth in depressive disorders via adenosine receptors. Inosine is also used for treating sepsis in infections. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Inosine is a potent stimulator of nerve growth factor (NGF) induced neurite outgrowth. The elevated levels of inosine in brain following injury are associated with the increased expression proteins related to axonal regeneration and growth. Mice given inosine demonstrated enhanced recovery of fine motor control following ischemic brain damage. Inosine may be used in studies of the process A-to-I RNA editing. |
|
Purification Methods |
(-)-Inosine forms anhydrous crystals from aqueous 80% EtOH but the dihydrate from H2O. [Beilstein 31 H 25, 26 III/IV 2087.] |
InChI:InChI=1/C10H12N4O5/c15-1-4-6(16)7(17)10(19-4)14-3-13-5-8(14)11-2-12-9(5)18/h2-4,6-7,10,15-17H,1H2,(H,11,12,18)/t4-,6-,7-,10?/m1/s1
A series of ribo- and deoxyribonucleosid...
Oxazepam and lorazepam inhibit the adeno...
The 3'-C-branched-adenosine and 2'-deoxy...
In addition to the already known differe...
We report on the synthesis of two series...
Adenosine deaminase (ADA), which is a ke...
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency is ...
5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-D-[13...
A noncovalent RNA complex embedding an a...
The L-stereoisomer analogues of D-coform...
-
The hypothesis that life on Earth may ha...
Genomic sequence analysis of Acinetobact...
The bi-enzymatic synthesis of the antivi...
Nucleoside analogs represent a class of ...
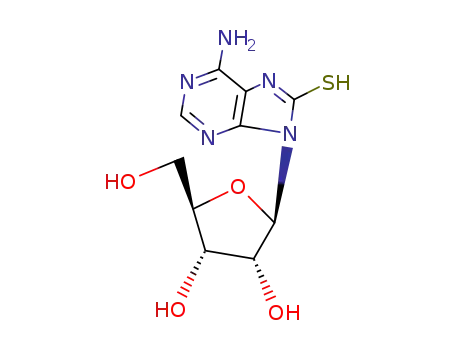
8-mercaptoadenosine

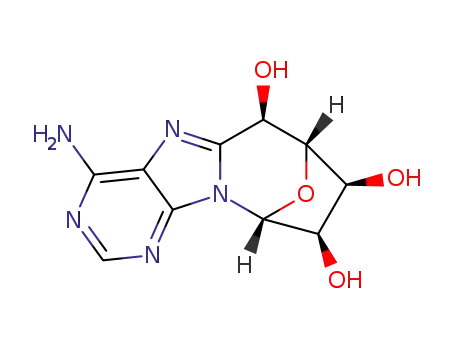
(5'R)-5',8-cycloadenosine
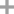
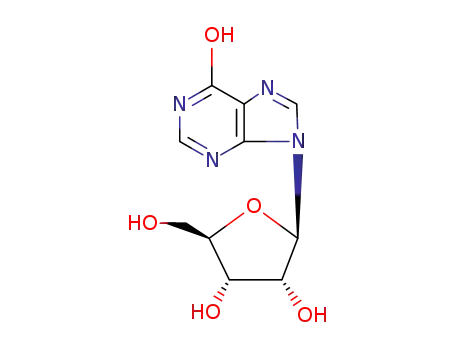
inosine

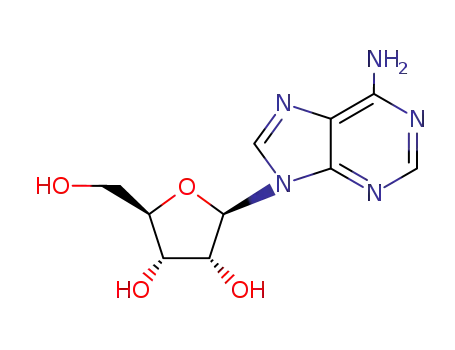
adenosine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogenchloride; sodium dihydrogenphosphate; water; sodium nitrite;
In
water-d2;
at 20 ℃;
pH=4;
Inert atmosphere;
|
71% 23% |
N6-aminoadenosine

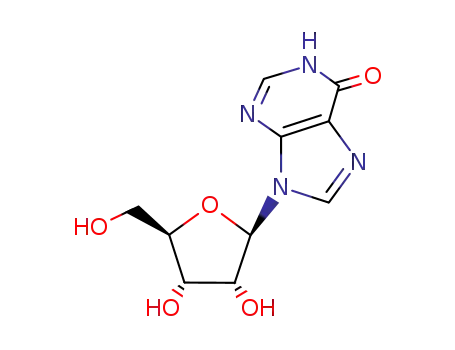
Inosine

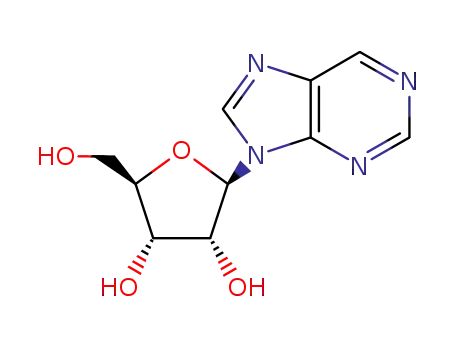
Nebularin


adenosine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
ammonia;
In
methanol;
|
15% 35% 40% |

adenosine
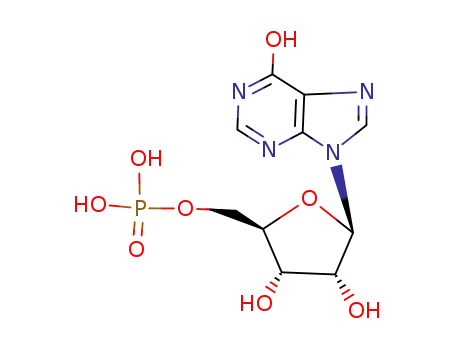
inosine-5'-monophosphate
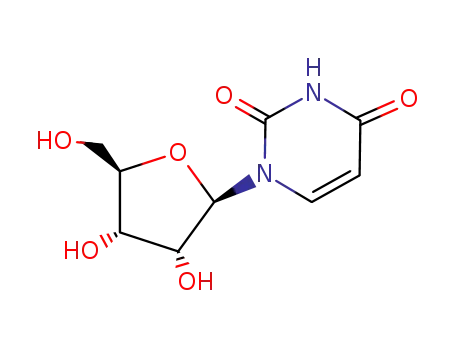
uridine
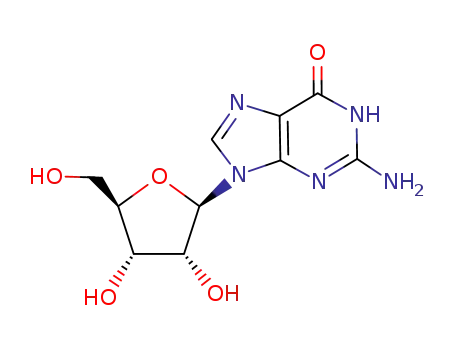
G
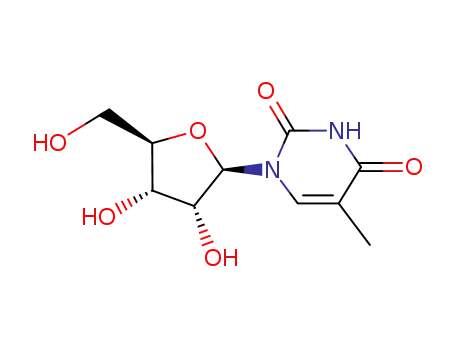
5-Methyluridine
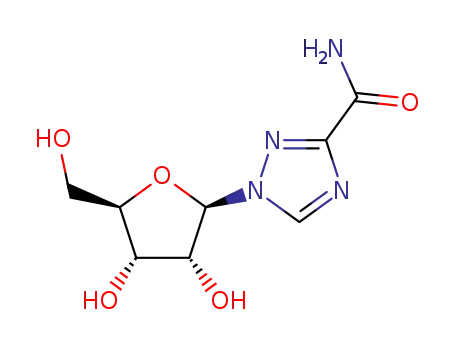
ribavirin
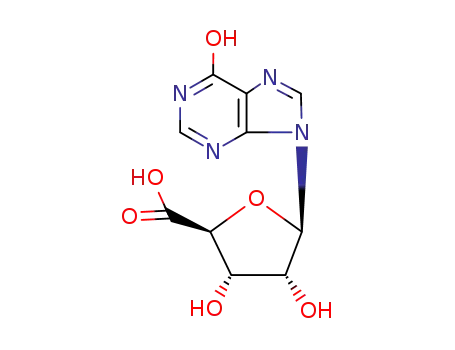
inosine-5'-carboxylic acid
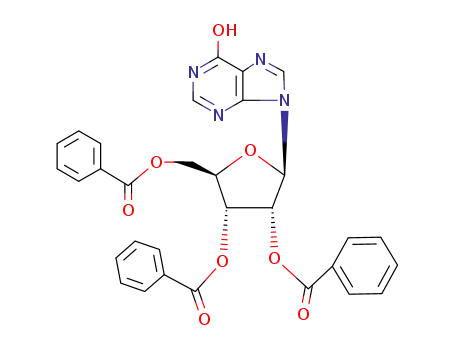
2',3',5'-tri-O-benzoylinosine
CAS:119356-77-3
CAS:868844-74-0
CAS:56553-60-7
CAS:55268-74-1